Taylor’s Historical Background
Scientific Management concept was developed by Fredrick Winslow Taylor. He was born in 1856. He was an American and began his career as a mechanist. He became popular through his theory of management and therefore also known as ‘Father of Scientific Management’.

While he was working in factories and mechanical shops he observed that owners and managers knew very little about what actually took place in the workshops. Taylor soon realized and believed that the system could be improved, and he looked around for an incentive. He settled on money. He believed a worker should get “a fair day’s pay for a fair days work” – no more, no less. If the person is unable to complete the target then he should not be paid. He also believed that both management and labour should cooperate and work together to achieve organisational goals. He was the first to suggest that primary functions of managers should be planning and training.
Taylor’s Scientific Management
Scientific Management means applying the scientific methods and tools to increase the output its quality and reduce costs and wastage. It is a systematic and thoughtful approach.
In words of Taylor, “Scientific Management means knowing exactly what you want from men to do and seeing that they do it in the best and the cheapest way”.
The concept of scientific management was given to improve the productivity, efficiency and effectiveness in the organization through the application of the proposed scientific principles and techniques.
Principles of Scientific Management
The philosophy of scientific management is based upon the following principles.

1. Science, not Rule of Thumb –
According to Taylor, each job should be performed in an organisation as per the scientific approach as these were developed after proper analysis and research. It should not follow rule of thumb which was based on trial and error method and approaches were based on intuition which was not suitable for modern business. When science is applied instead of the rule of thumb, to any job, it standatdizes work and help workers get a specialised way of performing task by avoiding wastage of time, cost and other valuable resources.
2. Harmony, not Discord –
Taylor emphasised on maintaining harmony between the management and workers in the workplace. This will avoid conflict and will promote friendly relationship among them which can result in improvement and growth in productivity of both labour and managers. He also said that there should be a transformation in thinking of both parties, which implies that management should share the gains with workers and workers should work hard for the betterment of business.
3. Cooperation, not Individualism-
This principle is an extension of principle of harmony. Competition should be replaced by cooperation. Management and workers both should Realise that they need each other. For this, management should entertain the constructive suggestions of employees and at the same time, workers should also cooperate with management. According to Taylor, there must be an equal division of work and responsibility between workers and management.
4. Development of each and every person to his/her greatest efficiency –
As per this principle, Taylor had the view that due concern should be given to increase efficiency. It could be built right from process of employee selection. Each person should be scientifically selected and then assigned work as per their specialization. He believed that employees should be give proper training of the task they need to perform because no human being is perfect, and there is always a scope of improvement. Hence training and development improve competency, skills and learning of the workforce. It is beneficial for both the organisation and the workers.
Techniques of Scientific Management
Following techniques were deployed by FW Taylor for manufacturing and production units:

1. Functional Foremanship –
Taylor developed the technique of functional foremanship. Under this technique, planning and execution are separated from each other. According to Taylor, single worker or supervisor cannot be expected to be an expert in all aspects. Thus, he advocated the appointment of eight firemen, out of which four will be responsible for planning and the rest four will be concerned with the execution of work.
Let us see the hierarchy under the functional foremanship –
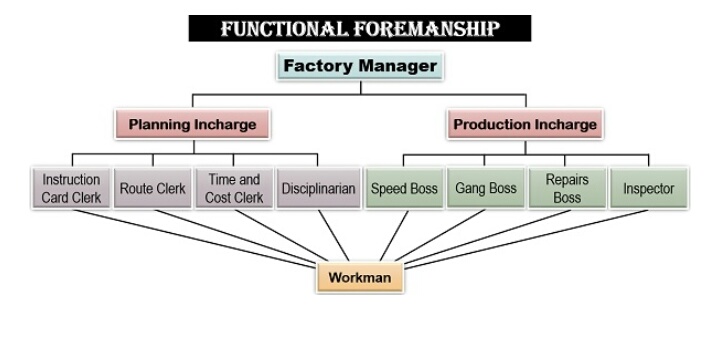
Factory Manager
A factory manager is a person who holds the highest managerial position in the unit and is responsible for the proper functioning of the organisation.
Planning Incharge-
A planning incharge is responsible for the formulation of policies, strategies and procedures of the operational activities. To simplify the work, following four clerks are appointed under the planning incharge.
a. Instruction Card Clerk:
The instruction card clerk will determine and direct how the work has to be performed.
b. Route Clerk:
A route clerk will decide what all is to be done and the steps which are to be taken to perform a particular task.
c. Time and Cost Clerk:
The person who determines the time limit in which the work is to be completed and the cost involved in carrying out each task is known as a time and cost clerk.
d. Disciplinarian :
A disciplinarian is a clerk who ensures discipline, follows rules and regulations and code of conduct in the organisation.
Production Incharge :
A production incharge needs to take care of all the operational and production activities. The four clerks assigned under a production incharge are as follows :
a. Speed Boss :
The speed boss is responsible for getting the work done on time.
b. Gang Boss :
The person w looks after the availability of all the equipment, tools and accessories is a gang boss.
c. Repair Boss :
The repairs boss has to take care of the repairs, maintenance and overhauling of the tools and machinery used for production.
d. Inspector :
The inspector is responsible for ensuring that all activities are being carried out in a planned manner. He/she also checks whether the quality of the products are as per standards or not.
Workman : He is a labour or worker at the operational level of the organisation who is responsible for actually performing the given task. Each worker is supervised and monitored by the eight different clerks, as mentioned above.
2. Standardisation and Simplification of Work :
Standardisation is the process of fixing well thought and tested norms with a view to maximize efficiency of work. Standardisation of product implies that the size, design, quality, shape etc of the product should meet the requirements and tastes of consumers.
Simplification means eliminating superfluous sizes, varieties and dimensions. It’s aim is to eliminate unnecessary diversity of products and thereby reduce costs. It will also help in achieving economy in the use of required machines and tools.
3. Work Study :
Taylor emphasised on examining and analyzing the working at the operational level of the organisation. It develops a systematic course of action and resolves the problems faced by labours and workers who are responsible for accomplishing the given task and duties.
Under this technique there are following four significant concerns of the organisation :
a. Method Study :
The managers come across numerous ways of performing a particular task or carrying out the production of goods or services. Out of all these possible methods, selection of the most appropriate way, which is cost effective and also increases the production is considered a method study.
b. Motion Study :
The motive behind conducting this study was to determine the movement of workers while performing a job. According to Taylor, it is necessary to analyze the movements of workers like how many times he lifts the objects, puts the objects because all these movements sometimes delay the work. Thus this study helps in knowing the productive and unproductive motions.
c. Time Study :
Analysing the time consumed for carrying out the given task in a specified manner is Taylor’s another scientific management technique which is called a time study. If an activity takes more time than the defined standard, it may lead to delay and decline in productivity. And if a task is accomplished much before the given time, it may lack efficiency.
d. Fatigue Study :
If an individual keeps on working without rest or pauses, it affects their health and efficiency. Therefore, fatigue study originated. This study seeks to find out the amount and frequency of rest intervals in completing a task. The objective of study is to find out how long a person can perform the standard task without any adverse effects on his health.
4. Differential Piece Wage System :
Taylor strong advocated piece wage system. He wanted to differentiate between efficient and inefficient workers. Under this system of wage payment, wages are paid on the basis of work done. According to him, higher rates were given to the workers who are producing standard products or more and lower rates were given to those who are producing less. Hence he talked about performance based remuneration and incentive based motivation.
5. Mental Revolution :
Taylor gave a powerful concept on changing the perception and attitude of both the employees and the management. They should both work together considering each other as family. There must be proper coordination and understanding among workers and the management in order to achieve organizational goals. Both of them must value efforts of each other and work together, creating a positive environment to achieve common organisational goals and objectives.