Buchner funnels are essential for laboratory filtration, separating solids from liquids. Named after the German chemist Ernst Buchner, these funnels have become a staple in chemistry, biology, and industrial labs worldwide. Selecting the proper Buchner funnel for your experiment improves efficiency and accuracy of filtration.
Understand the Purpose of Your Experiment
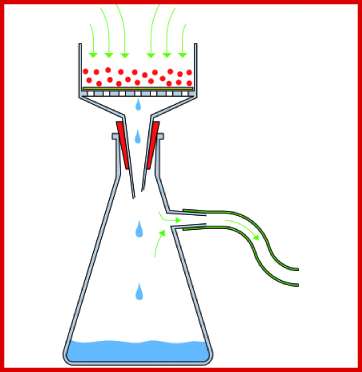
Before diving into the specifics of Buchner funnels, it’s crucial to define the goal of your experiment. Are you working with small-scale organic synthesis, large-scale crystallization, or microbiological filtration? The nature of your experiment will dictate the funnel’s size, material, and compatibility requirements.
Key considerations:
- Volume of the solution- Larger volumes require a funnel with a greater capacity.
- Type of filtration- Vacuum filtration processes work best with Buchner funnels designed to withstand pressure changes.
- Chemical compatibility- Ensure the funnel material can handle the chemical properties of your solution.
Choose the Right Material
Buchner funnels are available in various materials, including porcelain, glass, and plastic. Each material has distinct advantages and limitations:
Porcelain
Porcelain is esteemed for its high durability and exceptional resistance to elevated temperatures, making it an indispensable material in various laboratory settings. Its robust nature can withstand rigorous conditions of experiments involving acidic or basic solutions, serving as a reliable choice for crucibles, evaporating dishes, and other lab apparatuses. However, while porcelain’s weight adds to its stability, it calls for proper handling to avoid chipping. Laboratories favoring long-term durability and thermal resilience often opt for porcelain despite its vulnerability to impact, reflecting its valued role in scientific research.
Glass
Glass is a fundamental material in laboratories, favored for its chemical inertness and clarity, which permits uninterrupted visual monitoring during experiments. This transparency is crucial for precise measurements and observations in high-precision work, such as titrations and chemical reactions. Glass equipment, including flasks, beakers, and pipettes, is essential for tasks requiring a clean and non-reactive environment. However, its fragility demands meticulous handling to prevent breakage. Despite this, the ability of glass to facilitate accurate experimental outcomes ensures its continued prevalence in scientific studies.
Plastic (e.g., polypropylene)
Plastic materials like polypropylene are valued in the laboratory for their lightweight, cost-effectiveness, and robustness against breakage. Polypropylene is particularly appreciated for its chemical resistance, making it suitable for storing many substances, excluding strong solvents and high-temperature applications. It is a popular choice due to the durability and stability for disposable lab ware, such as test tubes and storage containers, which do not require glass or porcelain thermal stability. While it cannot withstand extreme conditions, polypropylene’s practicality in routine lab procedures makes it indispensable for modern scientific practices.
Choose the material based on your lab’s environmental conditions and the substances you are working with.
Select the Appropriate Size
Buchner funnels come in various sizes, typically measured by the diameter of the funnel head. The size you select should align with the following:
- The volume of liquid to be filtered- Ensure the funnel is large enough to accommodate the solution without frequent refilling.
- Vacuum flask compatibility- Check that the funnel fits securely onto the neck of your flask.
- Filter paper size- The diameter of the funnel should match the filter paper to avoid leaks or inefficiencies.
Standard diameters include 60 mm, 90 mm, 150 mm, and more significant for industrial use.
Consider the Type of Filter Paper
The filter paper you choose should correspond to the funnel size and the type of filtration required. Key factors include:
- Pore size- Determines the particle size that can pass through. Smaller pores are ideal for fine filtration, while larger pores allow faster flow rates.
- Material—Depending on chemical compatibility and thermal resistance needs, Options include cellulose, glass fiber, or synthetic materials.
- Pre-cut or custom cut- Pre-cut papers ensure a precise fit, while sheets allow size adjustments.
Evaluate Vacuum Compatibility
One of the primary advantages of a Buchner funnel is its ability to perform vacuum filtration. Ensure your funnel is:
- Designed to withstand the reduced pressure of a vacuum setup.
- Paired with a compatible vacuum pump and flask.
- Equipped with rubber adapters or seals to prevent air leakage.
Vacuum filtration significantly accelerates the process, making it essential for time-sensitive experiments.
Account for Budget Constraints
While quality should never be compromised, budget considerations often play a role in selecting lab equipment. Here’s how to balance cost and performance:
- Invest in durability- Porcelain and glass options comes with a higher upfront cost but is cost-effective in the long run.
- Evaluate disposables- Disposable plastic funnels might be more practical for low-cost experiments or hazardous substances.
- Bulk purchases- Purchasing bulk can reduce costs if your lab frequently uses Buchner funnels.
Wrapping Up
Choosing the proper Buchner funnel is more than picking the correct size or material. It requires a holistic approach, considering the specifics of your experiment, chemical compatibility, and safety standards. By evaluating your needs and matching them to the features of available funnels, you’ll ensure a smoother, more efficient filtration process.








