🌿 What is Biocomputing?
Biocomputing is an exciting and emerging field that combines biology and computer science to create systems that can process information using biological materials—like DNA, proteins, or cells—instead of traditional silicon chips.
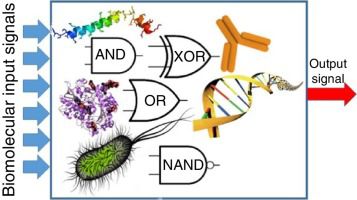
In simple terms, biocomputing uses living systems to perform computations. Just as electronic computers use binary code (0s and 1s), biocomputers use biological molecules that interact according to the laws of chemistry and biology to store and process data.
🧬 Key Areas of Biocomputing
- DNA Computing: Uses DNA strands to solve complex mathematical problems faster than conventional computers.
- Protein-Based Computing: Utilizes the folding and behavior of proteins for data storage and logic operations.
- Cellular Computing: Employs engineered cells that respond to stimuli and make “decisions” — useful in medical diagnostics.
⚙️ Applications of Biocomputing
- Medicine: Smart drug delivery systems that activate only when needed.
- Environmental Monitoring: Biosensors that detect toxins or pollutants.
- Data Storage: DNA can store vast amounts of information in microscopic space.
- Artificial Intelligence: Bio-inspired neural systems that mimic the human brain.
🌎 Importance and Future
Biocomputing offers a sustainable, energy-efficient alternative to traditional computing. As silicon-based technology reaches its physical limits, biological computing could revolutionize how we process information, diagnose diseases, and even repair the environment.
It’s not just the future of computing—it’s the future of life-inspired intelligence. 💡

